About E-business Suite
About Oracle IaaS
Infrastructure-as-a-Service Overview
- Oracle’s Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) provides a complete infrastructure for enterprise workloads, including
- Compute services
- Storage services
- Network services.
This enables you to run any type of workload in the cloud and in particular run Oracle workloads in the most optimized way.
Why run EBS on Cloud
- Retains all the benefits On-Premise EBS
- Same EBS applications
- Ability to customize or maintain
- Skills/competencies
- Cost benefits
- Scalable
- Faster time-to-market
- Increased business agility
- Lower risk
Offerings available
The following features are now available:
- Quick Provisioning
Quick Provisioning is the fastest way to provision a new Oracle E-Business Suite instance on Oracle Cloud by leveraging the various machine images available in the Oracle Cloud Marketplace.
- Lift and Shift
Copy (or clone) an on-premises environment to Oracle Cloud, use it for testing or development, or migration of your production environment to the cloud.
You can copy your entire on-premises EBS environment to the Oracle Compute Cloud Service (IaaS)
EBS use cases
- Scenario One – Customers planning to upgrade can use it for quick provisioning and testing.
- Use Quick provisioning to get a Vision instance, or
- Use Lift & Shift to move a clone.
- Scenario Two – Use it for Dev or Test environments.
- Use quick provisioning to start from a blank instance.
- Use lift & shift to move a clone.
- Scenario Three – Use it for Gold instance.
- Scenario Four – Use it for Production.
Cost estimation
- Oracle cloud price list for different applications can be checked for various offers provided by Oracle on cloud services.
- Effort estimation to install Oracle ebiz R12 instance on IaaS platform is about One day including time for creating storage with Ebiz image which is could take few hours depending on the size of the image.
- Creating storage from Ebiz image is the longest step.
Service Effectiveness
Easiness: Working on Cloud domain seems quite easy. All the applications are well organized and available to choose. You just need to select proper applications and create as per your requirement.
Storage creation takes sometime but other things can be installed and created quite fast. Moreover if something is done wrong you can anytime rollback or delete the changes you have done previously very easily.
Based on the need of the customer or number of users, utilities can be increased or decreased very easily.
Performance: Initial few setups take some time to load (Like Storage creation) otherwise all the steps are very fast. Oracle apps forms were opening normally without any delay. Load performance can’t be checked but as I mentioned based on number of users, resources can increased/added very easily to enhance performance.
Steadiness: Our experience with instance creation was that instance was running quite steadily. There were no network delays or services delays while working on oracle apps. Normal internet speed is needed to run applications. There might be network delays if internet speed is slow.
Installation brief
Basic activities performed for Oracle apps R12 installation on IaaS platform are:
- Oracle apps Installation Image download
- Storage creation
- Network activities(SSH key generation and security rules)
- Instance creation
- Configuration and startup of EBS instance
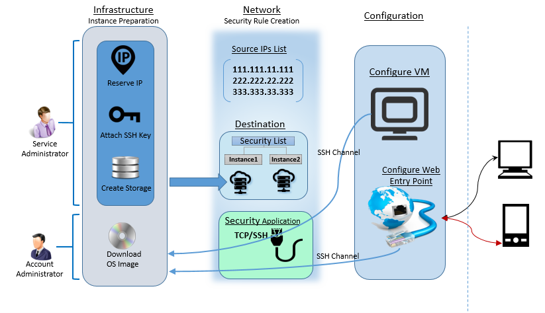
Pictorial view
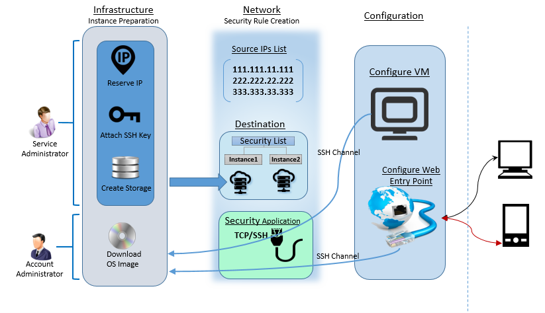
Oracle EBS Installation on Oracle Cloud IaaS
- Step#1: Setup access to Oracle IaaS cloud service.
- Step#2: Prepare and Create Cloud Server Instance.
- Step#3: Configure EBS instance and Startup.
Step#1: Setup access to Oracle IaaS cloud service
To install and use Oracle EBS instance on Oracle cloud IaaS, role you should have Cloud Service Administrator to administer Oracle Cloud Services within an identity domain owned by an Oracle Account of your company.
- Account Administrator
To start with IaaS on oracle cloud, you need an Oracle SSO account, along with Cloud “Account Administrator” access. Once you have these privileges you can navigate to cloud account dashboard using http://myaccount.cloud.oracle.com, where you can enter Oracle SSO account credentials to access cloud account.
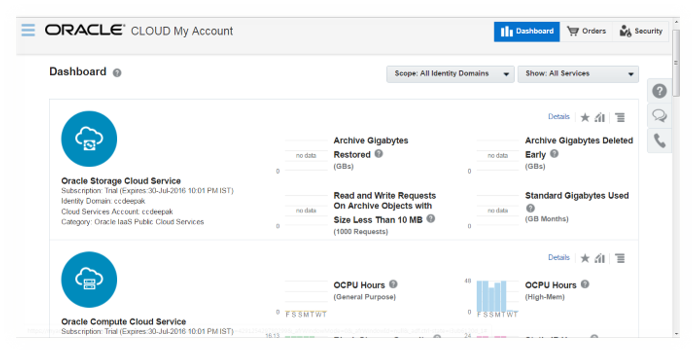

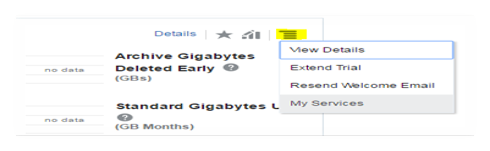
To navigate to Service Administrator dashboard, you can click on any one of the dashboard item’s Action link to navigate to My Services dashboard.
- Service Administrator
If you have Service Administrator role, then you can enter credentials for the logged in account to access My Services dashboard. There are two ways to access Services Dashboard.
- Use http://myservices.us.oraclecloud.com and provide a domain name and click on Go button to go to Sign on page.
- Use My Services action navigation from Account Dashboard, to directly go to the Sign on page. On the sign on page to change the identity domain you can click on change domain link and provide appropriate domain name.
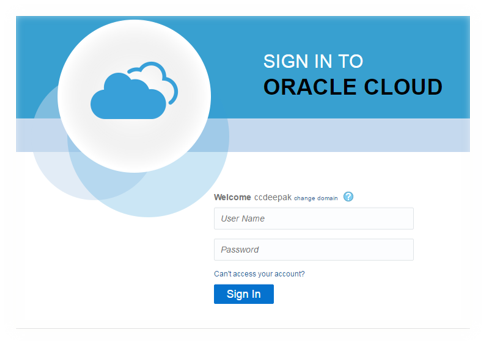
Enter credentials to access My Services Dashboard.
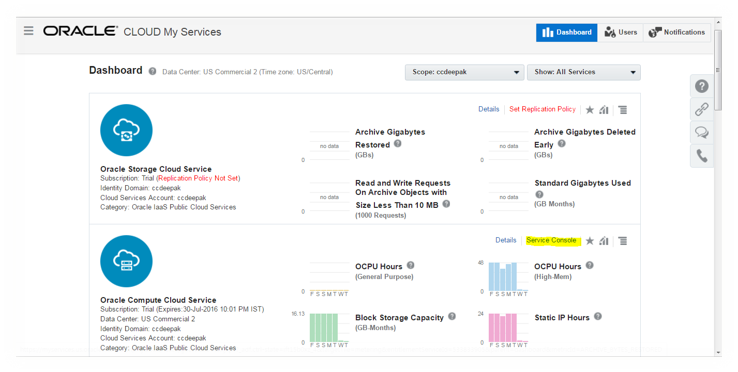

On the services dashboard, click on Service Console (highlighted in yellow in Figure 4) for Oracle Compute Cloud Service to navigate to Compute Services details, where you can setup instances.
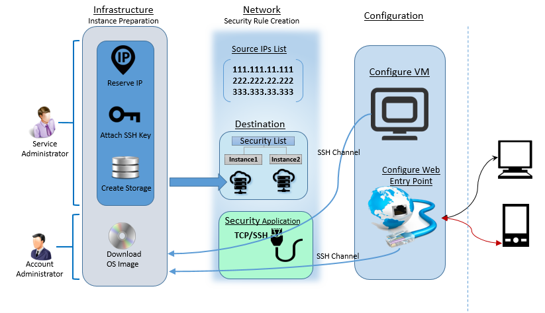
Step#2: Instance preparation
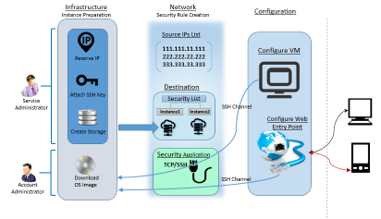
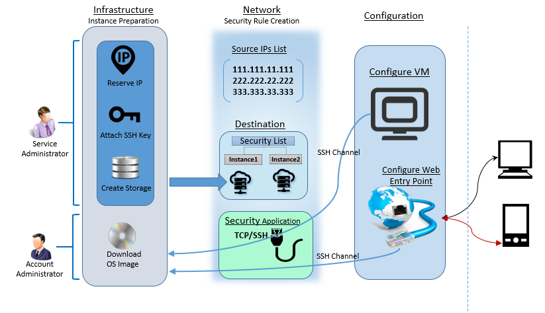
Account and service administrators can start with a sequential list of steps to have the instance prepared on Oracle Cloud. Among these steps, Downloading OS image to Oracle account and creation of data storage are the most critical steps and takes few hours. Account administrator downloads OS image into the account. Service administrator creates storage, network components such as Security Rules and its constituent sub components. The instance is created over a storage using the downloaded image along with an SSH Key and a reserved IP. The entire process of creating an instance comprises of a set of sequential steps as shown in below figure.
Step#2.1: Download image to the account
Step#2.1: Download image to the account
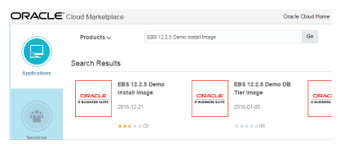
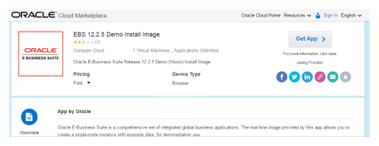
To download an OS image to your oracle account, search for the image in oracle cloud market place. Use URL https://cloud.oracle.com/marketplace to access products in cloud market place. Search for the image that you want to install. In this case it would be EBS 12.2.5 Demo Install Image. Click on EBS 12.2.5 Demo Install Image to go to the details page and then click on “Get App” button as shown below. If you are already logged in this will take to terms agreement screen, where you have to agree on the terms, if you are not logged in you would have to go through SSO login process.

The download process takes an hour or two. After successful download the service administrator can see it under images tab in service console. This image can be further used in cloud instance creation.
Step#2.2: Create storage
Step#2.2: Create storage
Login to service console and navigate to storage tab. This tab displays all the storages that were created by the service administrator for your account. Click on Create Storage Volume and proceed further to create storage.

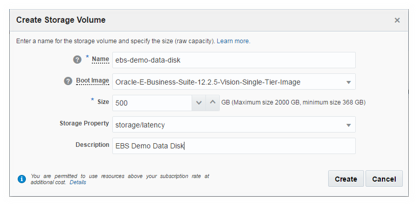
On create storage volume page, enter appropriate values and then click on create button. For EBS 12.2.5 please allocate 500 GB of storage space, and select the image downloaded in the previous step. After creation you will see a confirmation message and the instance will be listed under storage tab.

Step#2.3 SSH Key
SSH Key is needed to access the cloud instance over SSH protocol. This is a two step process where you create an SSH Key, then secure the instance by adding the public key and communicating to the instance using private key.
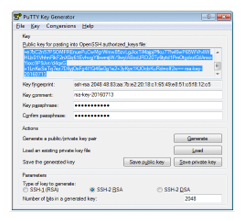
Step#2.3.1 Create SSH Key
Create an SSH key from your computer using PuTTY Key Generator. Store public and private keys for later usage. Public key content is used while Adding SSH Public Key from service console. The private key file is used to access cloud instance over SSH protocol. While creating SSH Key make sure to enter key passphrase. Key passphrase is needed while trying to access the cloud instance over SSH protocol.
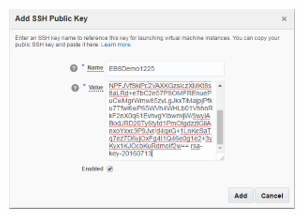
Step#2.3.2 SSH Public Key
Navigate to Network tab under service console and add public key. While adding public key paste the public key content created above. Make sure that the entire public key content is copied and pasted while adding the SSH Public Key.
Step#2.4 Reserve an IP
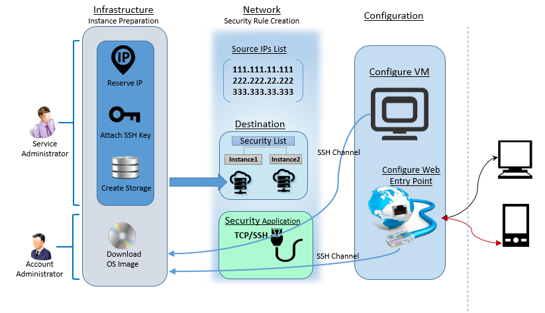
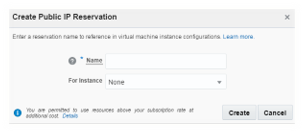
Navigate to Network tab under service console and then to the IP reservation sub tab. Click on Create IP Reservation. This IP will be assigned as a public IP to the cloud instance. Provide an appropriate name for the IP Reservation, the IP address will be automatically assigned. You can leave instance drop down None for now, as the instance is yet to be created.
Step#2.5 Security rules
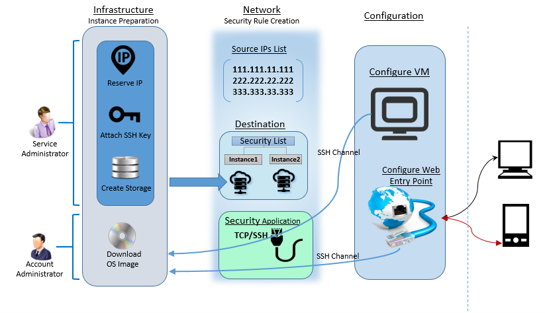
Step#2.5 Security rules (White list IPs)
Security rules are used to control network access between internet and the cloud instance. Security rule defines possible source of communication to the cloud instance over a specific port and protocol type. Before creating a security rule you need to have source IP list, destination instances list and security application (port and protocol pair).
Step#2.5.1 Security List
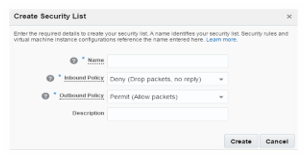
You can have a new security list created or use an existing security list if one exists. The security list is a list to which the instance can be added. This security list acts as a firewall for inbound and outbound communications to the list of instances attached to this. You can restrict inbound and outbound access privileges within the security list. These lists can be configured as destination within the security rule configuration.
Navigate to Network tab under service console, and then to Security List sub tab. Click on Create Security List to create a new security list. Provide an appropriate name, and choose Deny for Inbound Policy and choose Permit for Outbound Policy.
Step#2.5.2 Security IP List
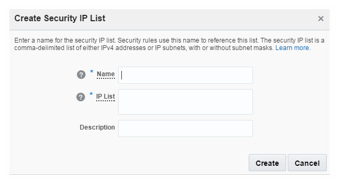
Security IP list holds a group of IP addresses or subnets from where there could be potential requests to cloud instances defined in the destination (security list) of security rule. This IP list is configured as source within the security rule configuration.
Navigate to Network tab under service console and then to Security IP List sub tab. Click on Create Security IP List to create a list. Provide an appropriate name, and list of IP addresses or subnets from where the cloud instance could be accessible.
Step#2.5.3 Security Application
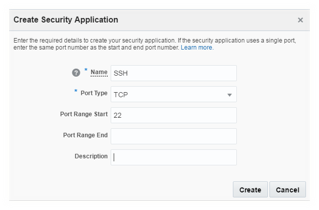
A security rule is defined for a specific pair of port and protocol type which is called a security application. Possible protocol types are TCP, UDP, ICMP and GRE. By default there exists on application with name all which is for all ports across all protocols. Security rule defined using all, lets all the ports open for all port types, which is not recommended.
Navigate to Network tab under service console Security Application sub tab. Click on Create Security Application. Provide an appropriate name, TCP as Port Type and 22 as Port Range Start. Optionally you can provide Range End as well.
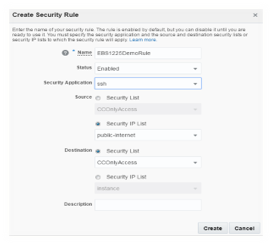
Step#2.5.4 Security Rules
Once you have Security List, IP List and application defined a security rule can be defined using these three components. Navigate to Network tab under service console, and then to Security Rules. Click on Create Security Rule. Provide appropriate Name, and keep the status Enabled so as to get this rule into effect. Select security application that was created in section 3.5.3, select the Security IP List created in section 3.5.2 as source and Security List created in section 3.5.1 as destination, and complete the process of rule creation.
Step#2.6 Create Instance
Oracle cloud instance is a virtual machine running a specific operating system, created using the image that was downloaded to your account, storage that was created by the service administrator, along with the network components that were configured. Preparation of instance is a five step process as shown below. Figure caption details each of the step.
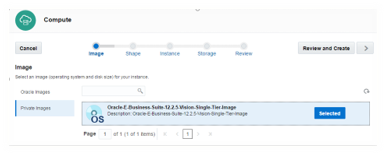
1: Select the downloaded OS image
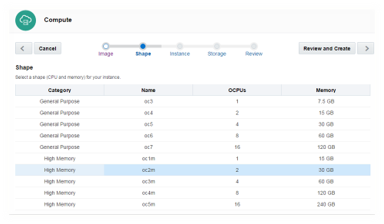
2: Select the CPU configuration
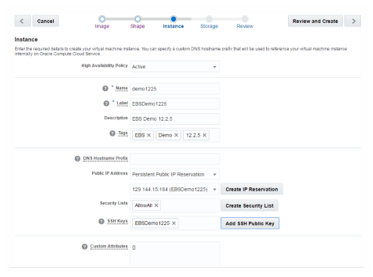
3: Provide Instance Name, Label, and Tags. Select Public IP address as “Persistent Public IP Reservarion” and select the IP reserved in step#2.4, select the security list created in step#2.5.1 and add the SSH key created in step#2.3.2. The navigate to next step(Storage) and click on Attach Storage.
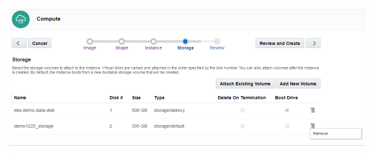
4: Attach the storage volume created in step 3.2. Attach this as Disk # 1, and select Boot Drive.
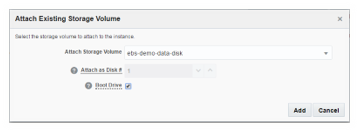
Remove the default boot storage volume that is added by the system
5: Review and create
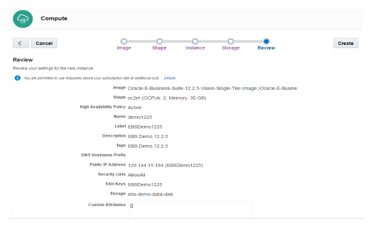

Finally review the instance details and proceed to creation.
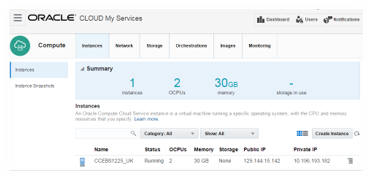
Instance creation process can take hours and you will receive a confirmation message upon successful creation.
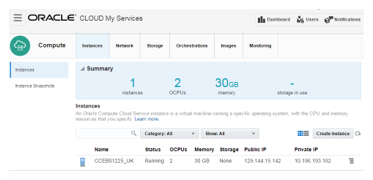

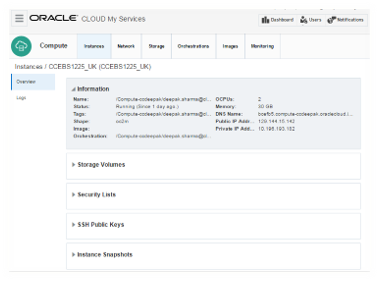
The instance details can be viewed in Instance tab under
service console.
Orchestration for the cloud instance:
An Orchestration is created along with the instance that maintains the interdependencies of different components involved in creation of the instance. For example the network components and storage can be created independent of the instance or in-line with the instance as part of the instance step in the instance creation train step process. If you delete the Orchestration that was created as part of the instance, it deletes the inline or dependent components along with the instance.
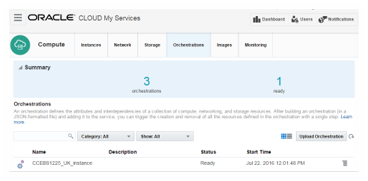
Step#3: Configure EBS Instance
Before you try to use the new Oracle E-Business Suite environment, you should confirm that virtual machine configuration is complete.
Step#3.1: VM Configuration
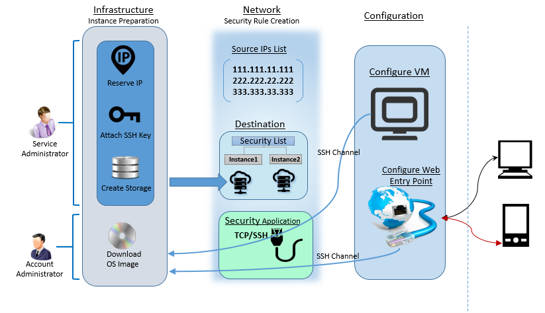
- Log into the instance using SSH
- Start Pageant.exe and add the private SSH Key created in step 2.3. This will provide the key information to Putty automatically.
- Now start PuTTY, and in the Host Name (or IP address) field, enter the public IP address of your instance.
- In the Connection type: field underneath the Host Name (or IP address) field, select the SSH radio button if it is not already selected.
2.Look for entries like these in the log file “/var/log/oraclevm-template.log” by executing below command.
-bash-4.1$ sudo vi /var/log/oraclevm-template.log
Expected result:
[INFO] Jul 13 16:36:46 configdhcp.sh: Configuring Database Tier
[INFO] Jul 13 16:44:04 configdhcp.sh: Cloning the DB Tier Completed Successfully
[INFO] Jul 13 16:44:04 configdhcp.sh: Proceeding with the Apps Tier Configuration
[INFO] Jul 13 17:57:04 configdhcp.sh: Cloning the Apps Tier Completed Successfully
- Confirm that following directories are available:
- /u01/install/APPS/12.1.0
- /u01/install/APPS/data
- /u01/install/APPS/fs1
- /u01/install/APPS/fs2
- /u01/install/APPS/fs_ne

- If you are utilizing a bootable storage volume and these directories are missing, indicating that Oracle E-Business Suite was not provisioned, follow this procedure to correct the mount point and complete the provisioning operation:
- Reboot the VM by running the ‘reboot’ command.
- Ensure that no database or application tier processes are running. If they are running, shut them down.
You can use “ps –ef | grep oracle” to find the processes and use “kill -9 pid” to kill the processes.
- As the root user, run the command:
$ /usr/sbin/oraclevm-template –config –force
- Wait till you get a confirmation in the /var/log/oraclevm-template.log file that cloning of both DB and Application tier is done.
- Reboot the VM by running the ‘reboot’ command.
Step#3.2: Configure Web Entry Point
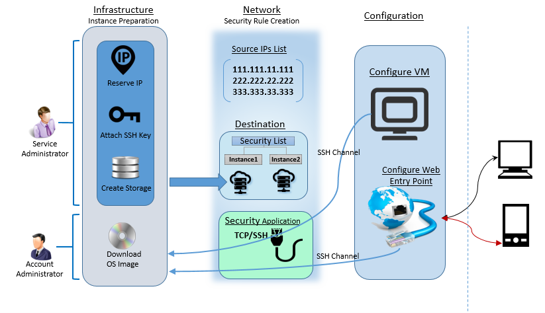
The Oracle E-Business Suite instance on Oracle Cloud is installed with an internal DNS name and a private IP address, so is not accessible from the public Internet. To make the instance accessible from the public Internet, you need to set the web entry point parameters in the applications context file to point to the publichostname.public domain name.
Perform the following steps to configure the web entry point.
- Identify the public IP address of your Oracle E-Business Suite virtual machine.
Note: You can find the public IP address by navigating to the Instances tab on the Oracle Compute Cloud Service console and reviewing the details page for your instance.
- If, for example, the public IP address of the virtual machine is 129.144.15.144, the public hostname.public domain for the virtual machine will be oc-129-144-15-144.compute.oraclecloud.com
3.Check that the Oracle E-Business Suite database tier services (database and TNS listener) are running. If they are not, start them by performing the following steps, first setting the user account to ‘oracle’ and then running the startdb.sh script:
- Log in as oracle and execute the /u01/install/APPS/scripts/stopapps.sh script to stop any application tier processes that are running.
- Log in as oracle and execute the /u01/install/APPS/scripts/startapps.sh script to start the application tier processes.
- Access the Oracle E-Business Suite Login page. For example:
http://oc-129-144-15-144.compute.oraclecloud.com:8000/OA_HTML/AppsLogin